What Is Polar Bond Example
A polar molecule has a net dipole as a result of the opposing charges ie. A classic example of a polar bond is the bond in water between hydrogen and oxygen.

Why Is Water A Polar Molecule Water Molecule Polarity Of Water Covalent Bonding
A polar covalent bond is a covalent bond in which the atoms have an unequal attraction for electrons and so the sharing is unequal.

What is polar bond example. A polar bond is a covalent bond between two atoms where the electrons forming the bond are unequally distributed. A hydrogen bond H-bond is a specific type of interaction that involves dipoledipole attraction between a partially positive hydrogen atom and a highly electronegative partially negative oxygen nitrogen sulfur or fluorine atom not covalently bound to said hydrogen atom. Covalent bonds in which the sharing of the electron pair is unequal with the electrons spending more time around the more nonmetallic atom are called polar covalent bonds.
A bond in which the electronegativity difference between the atoms is between 04 and 17 is called a polar covalent bond. This happens when there is a difference between the electronegativity values of each atom. This causes the molecule to have a slight electrical dipole moment where one end is slightly positive and the other is slightly negative.
In this type of bond one is sigma and other two is pi- bond formed by side to side overlapping. Non polar covalent bond. In a polar covalent bond sometimes simply called a polar bond the distribution of electrons around the molecule is no longer symmetrical.
For atoms with equal electronegativity the bond between them will be a non- polar covalent interaction. It is not a covalent bond but instead is classified as a strong non-covalent interaction. The bonding electrons in polar covalent bonds are not shared equally and a bond moment results.
A bond forms when the bonded atoms have a lower total energy than that of widely separated atoms. A non polar covalent bond is formed when two same atoms share electrons by head to head overlapping single covalent bond. For example in diatomic nitrogen NN the bond number is 3 in acetylene HCCH the bond number between the two carbon atoms is also 3 and the CH bond order is 1.
Substances such as NaCl and MgCl 2 are the usual examples. The bond is classified as a polar bond because it has a large electronegativity difference of 14. In a polar covalent bond sometimes simply called a polar bond the distribution of.
However a molecule may be polar or nonpolar depending on its geometry. When all of these dipoles are taken into consideration in three dimensions the uneven distribution of charge caused by the dipoles may cancel out. A diatomic molecule that consists of a polar covalent bond such as ceHF is a polar molecule.
The dipoles do not cancel out resulting in a net dipole. This last example is about as polar as a bond can get. An ionic bond is actually the extreme case of a polar covalent bond the latter resulting from unequal sharing of electrons rather than complete electron transfer.
An example of such a non-polar molecule is hydrogen H 2. In larger molecules with multiple covalent bonds each bond will have either no dipole or a dipole with varying degrees of partial charge. In non-polar covalent bonds the electrons are equally shared between the two atoms.
Difference in EN 2 CH bonds relatively nonpolar C-O C-X bonds more electronegative elements are polarelectronegative elements are polar Bonding electrons shift toward electronegative atom. Polar Bond Definition. The binding arises from the electrostatic attraction of their nuclei for the same electrons.
Having partial positive and partial negative charges from polar bonds arranged asymmetrically. A bond in which the electronegativity difference between the atoms is between 05 and 21 is called a polar covalent bond. As mentioned in section 47 because the electrons in the bond are nearer to the F atom this side of the molecule takes on a partial negative charge which is represented by δ δ is the lowercase Greek letter delta.
Unlike an ionic bond a covalent bond is stronger between two atoms with similar electronegativity. Bond Polarity and Inductive EffectBond Polarity and Inductive Effect Nonpolar Covalent Bonds. Electronegativity is probably the most important concept to understand in organic chemistry were going to use the definition that Linus Pauling gives in his book the nature of the chemical bond so Linus Pauling says that electronegativity refers to the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself so if I look at a molecule Im going to compare two atoms in that molecule Im.
Example Nonpolar Covalent Bond is found in gas molecules like Hydrogen gas Nitrogen gas etc. It is denoted by three short lines. These proteases possess an active site serine whose R group hydroxyl generates a covalent bond with a carbonyl carbon of a peptide bond and results in the hydrolysis of the peptide bond.
For example the polar compound methyl alcohol has a negative pole made of carbon and hydrogen and a positive pole made of oxygen and hydrogen see Fig. In such a bond there is a charge separation with one atom being slightly more positive and the other more negative ie the bond will produce a dipole moment. The electrons are unequally shared with the oxygen atom spending.
The rule is that when the electronegativity difference is greater than 20 the bond is considered ionic. A water molecule abbreviated as H2O is an example of a polar covalent bond. An extreme difference forms an ionic bond while a lesser.
A polar covalent bond is a covalent bond in which the atoms have an unequal attraction for electrons and so the sharing is unequal. For example tetrachloro-methane carbon tetrachloride CCl 4 has polar CCl bonds but the tetrahedral arrangement of the four bonds about the central carbon atom causes the individual bond moments to cancel. Covalent bond in chemistry the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms.
When molecules are symmetrical however the atoms pull equally on the electrons and the charge distribution is uniform. Atoms with similar EN Polar Covalent Bonds. The electrons in hydrogen are more attracted to the electrons in oxygen because oxygen is more electronegative.
So the question that comes to mind is If the process for dissolution is going to be the same for polar or nonpolar molecules and crudely the same for molecules with hydrogen bond and for ionic compounds why are some solutes insoluble in some solvents. Water H 2 O is an example of a polar molecule since it has a slight positive charge on one side and a slight negative charge on the other. Polar Molecules.
Ionic bonds typically form when the difference in the electronegativities of the two atoms is great while covalent bonds form when the electronegativities are similar. Polarization of Covalent Bonds It is observed that in the sigma bonds between two different atoms the electron cloud is always closer to the more electronegative of the two atoms participating in the sigma bond. Depending on polarity 1.
The charge of the electric dipoles is less than a full unit charge so they are considered partial charges and denoted. The best example of this involves proteolysis by serine proteases that have both digestive enzymes and various enzymes of the blood clotting cascade. Bromine water is an example for a start but certainly not the most remarkable example.
Bond number gives an indication of the stability of a bond. This type of bond occurs when there is complete transfer between the two atoms of the electrons in the bond. Polar molecules occur when two atoms do not share electrons equally in a covalent bondA dipole forms with part of the molecule carrying a slight positive charge and the other part carrying a slight negative charge.
In H-H each H atom has an electronegativity value of 21 therefore the covalent bond between them is considered nonpolar Polar Covalent Bond A bond between 2 nonmetal atoms that have different electronegativities and therefore have unequal sharing of the bonding electron pair. Difference in EN of atoms 2 Ionic Bonds.

How Do Molecular Compounds Bond Example Hydrogen Bond Bond Covalent Bonding

Ionic Bond Definition Examples Formation Digital Kemistry In 2021 Ionic Bonding Chemistry Ap Chemistry

Definition And Examples Of A Polar Bond In Chemistry Covalent Bonding Chemical Bond Chemistry

Polar And Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Definitions And Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Electron Configurations The Periodic Table Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Education

Difference Between Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Definition Formation Properties Examples Covalent Bonding Study Chemistry Chemical Bond

Biology Polar Vs Nonpolar Bonds Expii Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Quotes Chemistry Education

Ionic And Covalent Bonding Are Depicted In The Picture Ionic Bonds Is The Attraction Of A Cation To An An Ionic Bonding Teaching Chemistry Covalent Bonding

Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Covalent Bonding Chemistry Lessons Molecules

Chemistry Intermolecular Forces Polar Bonds And Polarity Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Education

Polar Vs Nonpolar Covalent Bonding Medical Student Study Science Chemistry

H 2 Hydrogen Gas Covalent Bond Bonds In Biology Weak Bonds Hydrogen Bonds Attraction Between And Hydrogen Bond Covalent Bonding Chemistry Basics

About The Mcat Mcat Chemistry Chemical Reactions Ciencias Quimica Quimica Cine En Casa

Details Here Https Dantuckerautos Com Fresh Protons In Carbon Covalent Bonding Polar Graphics Design Ideas
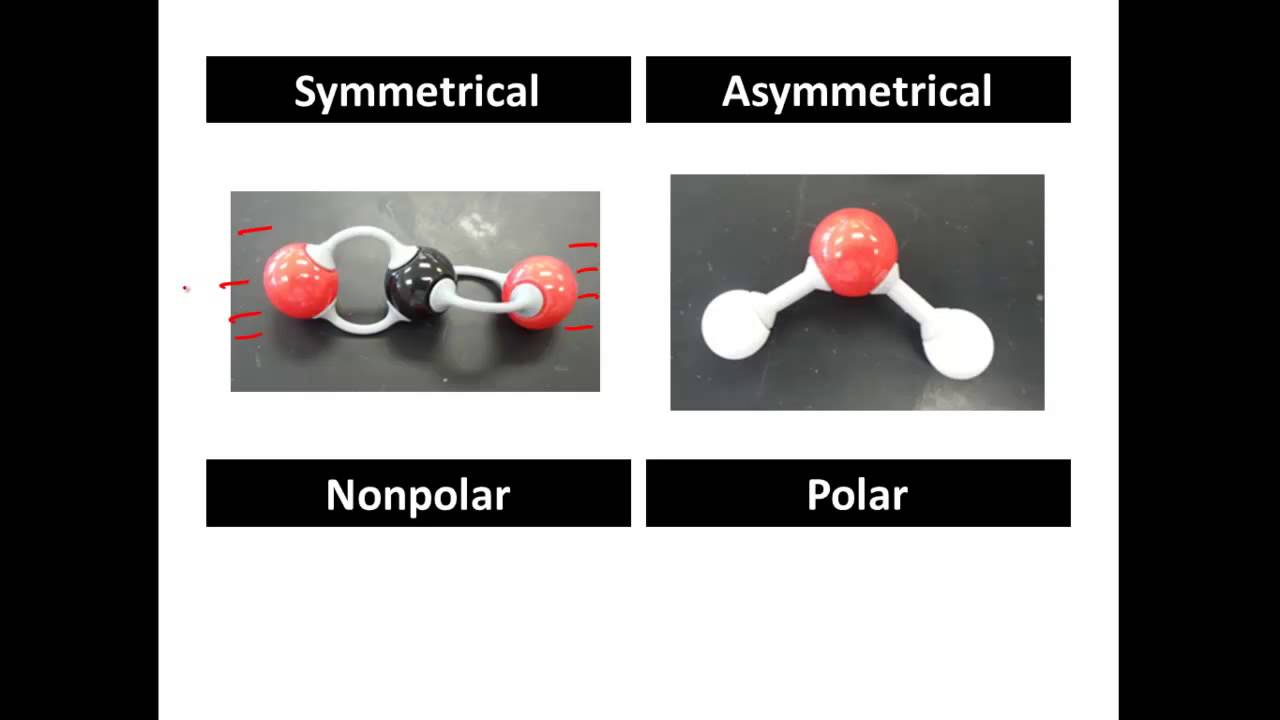
Polar And Non Polar Covalent Molecules Polar Vs Nonpolar Youtube Playlist Science Chemistry Molecules Chemistry

How Is Covalent Bond Is Formed A Plus Topper Formationofcovalentbond In 2021 Covalent Bonding Chemistry For Kids Bond

Chapter 2 Summary Science Chemistry Teaching Chemistry Chemical Structure

Difference Between Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

Bond Polarity Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Classroom
No comments for "What Is Polar Bond Example"
Post a Comment